Latest news

Your ECCS membership advantages
The ECCS - European Convention for Constructional Steelwork is offering annual memberships for all civil and structural engineers, especially in the field of steel construction.
Memberships are offered as individual, company and associate memberships and offer a broad variety of benefits for the joining members. One key advantage is the subscription of the quarterly published journal Steel Construction - Design and Research. In addition to the printed copy you will receive online access to the journal articles on Wiley Online Library.
For more information on the benefits and how to apply please see the ECCS website.

Mauerwerk - European Journal of Masonry 06/15
Cover Story: The listed Waterways and Shipping Office being built in the year 1895 is located on the Kiel- Holtenau sluice island, was restored by preserving its historic appearance and renovated energetically. Lastly, the old building, built in Wilhelminian brick architecture, did not fulfil the requirements for a modern office and administration building any more. (s. p. 487 to 490 ).
(photo: Ulrich Hoppe, Hamburg)

Geomechanics and Tunnelling 06/15
News about the Southern line - current state, processings and challenges of the Baltic-Adriatic corridor
- Koralmbahn quo vadis – Current state of the new Koralmbahn line and essential milestones
- Granitzta tunnel chain - Current state
- St. Kanzian tunnel chain - Current state of design and construction
- Semmering Base Tunnel - Approval and contracts

Structural Concrete Issue 04/15
Cover Story: The 2.815 m long, four-lane Laguna Bridge, also known as the Anita Garibaldi Bridge, will be Brazil’s third longest bridge and will significantly improve the transport connection from north to south to other South American countries. (© DSI, see pp. A5f.)
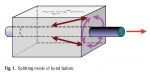
Structural Concrete 1/2015: Bond and anchorage of embedded steel reinforcement in fib Model Code 2010
This paper describes the changes to design provisions for embedded steel reinforcement in the fib Model Code for Concrete Structures 2010. The changes introduce new coefficients for steel grade and clear spacing between bars, and extend the range of concrete strengths covered. The way in which the contribution of hooks or anchorages is calculated has been revised and the contribution of end bearing to laps and anchorages of compression bars is recognized. The revised rules represent a move away from a distinction between laps and anchorages per se towards a distinction based on the presence or absence of transverse pressure perpendicular to the bar axis within the bond length. The benefits of staggering laps with only a proportion of bars lapped at a section are also reviewed. Finally, the potential impact of lap and anchorage performance on structural robustness is discussed, and it is concluded that this can only be achieved if bar yield precedes splitting mode bond failures.
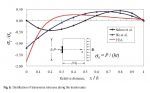
Structural Concrete 1/2015: Further investigation of transverse stresses and bursting forces in post‐tensioned anchorage zones
In the post-tensioned anchorage zone, the load transfer path of an anchor force can be visualized by an infinite number of isostatic lines of compression (ILCs). The method was initially proposed by Guyon and recently attracted significant interest from a number of researchers. Based on the work of these predecessors, an updated mathematical model has been proposed in order to analyse the bursting forces and the distribution of transverse stresses in the anchorage zone. Compared with the results of a finite element analysis, the updated equations are more accurate than the previous ones. Based on the observation that the sixth-order polynomial expression is better than the fourth-order one, as far as the solution of bursting stresses is concerned, it can be reasonably postulated that a de facto function of the ILCs must exist. Additionally, it is equally interesting that the bursting forces derived with the updated analytical model are the same as those obtained with the formula in the current AASHTO-LRFD Bridge Design Specifications based on numerical stress analyses.

Steel Construction 1/2015: Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures – Present status and further developments
Together with standards for fabrication and erection and harmonized product standards, the structural Eurocodes form the basis for the design of structures and structural products. From April 2010 onwards, the Eurocodes are obligatory for the design of structures and the national design codes have to be withdrawn.
Eurocode 3 covers design of steel structures. This paper gives an overview of the context in which Eurocode 3 exists and of the accompanying codes. The various individual parts of Eurocode3 are mentioned. Attention will be paid to the safety elements such as the partial safety factors for strength and stability. The National Annexes are discussed. Furthermore, corrections and amendments are mentioned and finally an opinion is presented on the possibilities and difficulties the practitioners will experience when using Eurocode 3 and on the future developments that are needed.
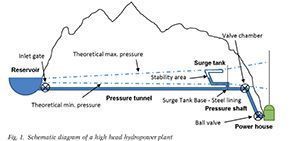
Geomechanics and Tunnelling 1/2015: Surge tanks for high head hydropower plants - Hydraulic layout – New developments
High head hydropower plants can generate high electrical power at very short notice, or if equipped with pumps can also draw electricity from the distribution grid and store its energy very efficiently. In this way, hydropower plants can make an indispensable contribution to regulating the grid and the use of regenerative energy sources. Physically, this requires reservoirs at various altitudes connected through headraces.
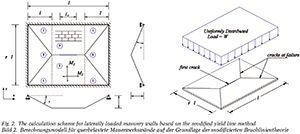
Mauerwerk - European Journal of Masonry 1/2015: The bending strength of masonry
Bending strength of masonry becomes an important design aspect especially when the walls subjected to lateral loads like, cellar walls which are subject to earth pressure, and façades/ infill walls which are exposed to the wind actions.
Bending strength is required wherever the applied load is perpendicular to the wall. It is also required in non-load-bearing partition walls, where the load applied in both the normal and perpendicular directions. Besides, the tensile properties of the brick/block and lengthwise parameters related to geometry and materials technology also influence the bending strength of masonry.

New publications autumn 2015
New publications from the areas: engineering and steel construction. You can find detailed information on the individual product pages.



